Craniosynostosis Surgery
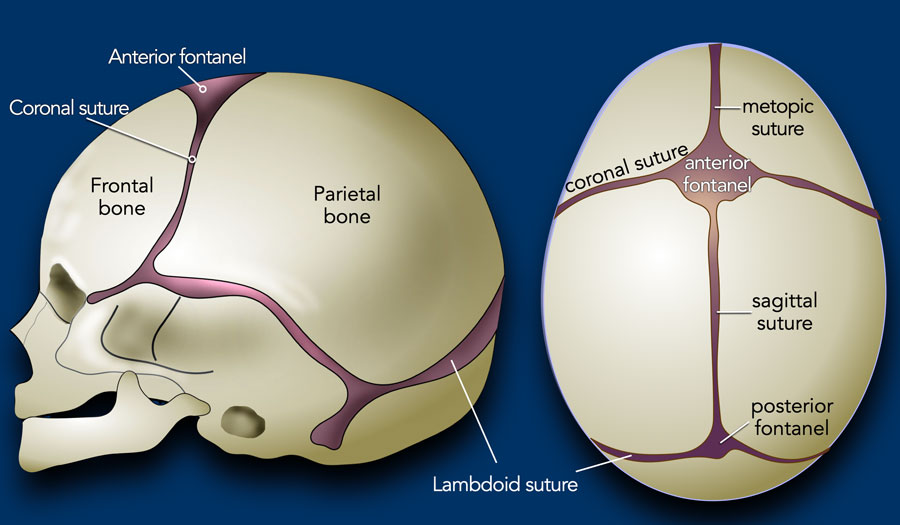
Craniosynostosis is a condition in which the fibrous joints between the skull bones close too early. These joints are called sutures. The bones surrounding the brain in the human skull have 6 main joints. If the suture closes prematurely (usually before or during birth), it can cause an abnormal head shape as well as facial deformity and symmetry. As the number of prematurely closing sutures increases, the pressure inside the head increases, causing the compressed brain to lose vision, hearing, etc. It may also cause negative effects on centers such as: vision and hearing loss. It may also cause retardation in mental-motor skills.
Surgical treatment of craniosynostosis is planned to correct the abnormal head shape and allow normal expansion of the chamber containing the growing brain. Craniosynostosis surgery is usually performed between 6-12 months of age. During this surgical treatment, different surgical techniques are applied depending on the needs and condition of the patient.
There are two important approaches: closed and open. In some cases, procedures such as bone lengthening/expansion are also performed with the help of a device called “distraction”. Closed surgical procedures, in which only closed sutures are opened (endoscopically), are unsuccessful, and additional surgical procedures may be needed afterwards. Since suture closure progresses from the base upwards and from the inside to the outside, it is important to intervene simultaneously in craniosynostosis surgery by anticipating possible disorders of the face and eye as well as the head and brain.
Craniosynostosis surgery; It is a complex procedure performed under general anesthesia by a plastic surgeon, neurosurgeon and an anesthesiologist experienced in this field. The surgery takes a minimum of 4 to 6 hours. It is important to use new surgical tools and techniques such as “piezo” during surgery to perform the procedure by an experienced team and to avoid possible complications. Intensive care is usually required in the early postoperative period to prevent any complications. After ensuring that the patient’s general health condition is good, the patient is taken to the normal ward and his monitoring and treatment continues. The patient is discharged approximately 3-5 days after the surgery. Follow-up and treatment are continued with regular checks.
What Can Craniosynostosis Surgery Treat?
- Abnormal head shapes resulting from premature suture closure
- Increased intracranial pressure (ICP) and restrictive obstacles to skull growth
- Eye and facial anomalies caused by premature suture closure
- Possible social exclusions that may occur in the future due to head and facial appearance
- Possible mental-motor development disorders that may occur due to inhibition of brain growth
Important Criteria for Craniosynostosis Surgery
- Most procedures to treat craniosynostosis are performed before the age of one.
- Almost every child whose sutures close prematurely is a candidate for surgery.
- Heart, kidney etc. Additional examinations are required for children with complex craniosynostosis or syndromic anomalies. The decision for surgical treatment in these patients should be made by a multidisciplinary team experienced in patients with complex craniosynostosis.
- Treatment of children with increased intracranial pressure/pupil edema and/or progressive vision-hearing loss is urgent.
Your child should be examined, the degree/content of craniosynostosis should be determined, and types of surgical procedures with options for the treatment of your child should be discussed together. Many times, some additional imaging and diagnostic methods such as 3D CT (Computed Tomography) scanning and 3D skull modeling may be needed to assist in diagnosis or to plan surgery.